Overview of Hurricane Beryl Spaghetti Models
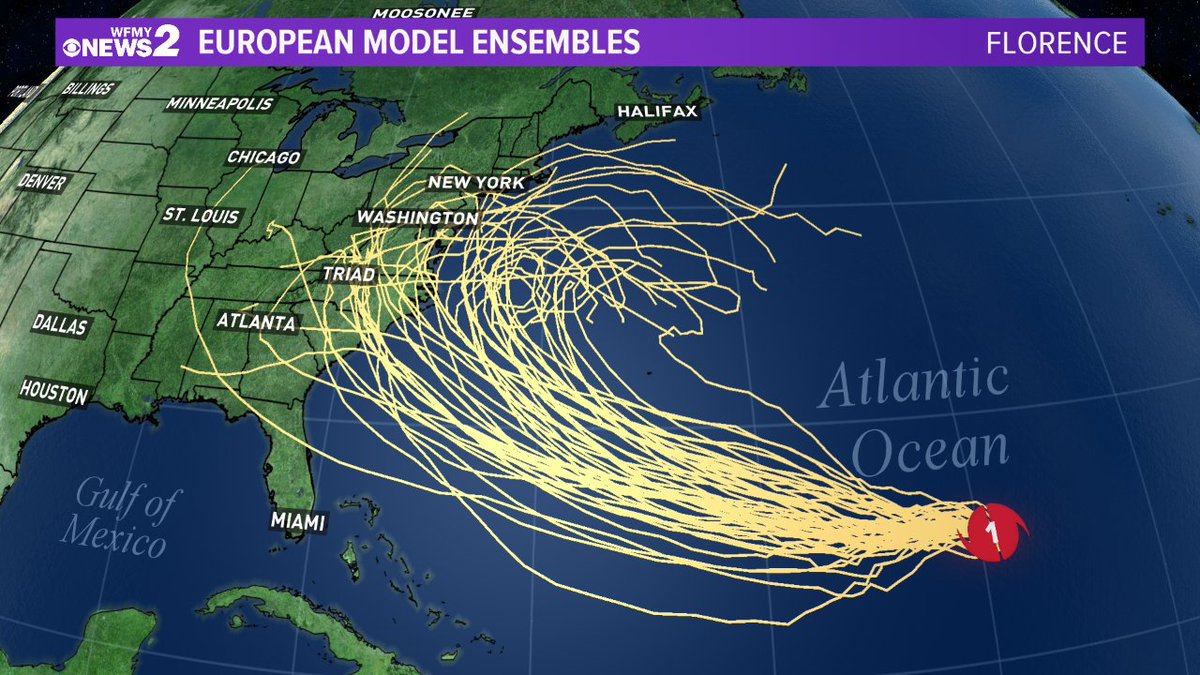
Hurricane beryl spaghetti models –
In the realm of hurricane forecasting, spaghetti models are indispensable tools that provide meteorologists with a comprehensive view of potential storm paths. These models, aptly named for their resemblance to a plate of spaghetti, depict numerous possible tracks that a hurricane may take, each represented by a thin line.
The swirling patterns of Hurricane Beryl’s spaghetti models danced across the screen, predicting its uncertain path. As we anxiously monitored its progress, a beacon of hope emerged in the form of Ian Machado Garry , a renowned meteorologist whose expertise illuminated the storm’s potential impact.
His insights calmed our fears and guided our preparations, reminding us that even in the face of nature’s fury, knowledge and resilience can prevail.
Spaghetti models are generated by computer simulations that incorporate a vast array of data, including atmospheric conditions, ocean currents, and historical hurricane behavior. By running multiple simulations with slightly different initial conditions, these models produce a range of possible outcomes, giving forecasters a probabilistic assessment of the storm’s trajectory.
The ever-changing hurricane beryl spaghetti models dance across the screen, their chaotic paths a reminder of nature’s unpredictable power. Yet, amidst the uncertainty, a beacon of hope emerges: the unwavering determination of meteorologists like Eric Gordon . With every update, their tireless efforts bring clarity to the storm’s path, guiding us through the tempestuous seas and towards a brighter horizon.
Interpreting Spaghetti Models

Spaghetti models are a valuable tool for understanding the potential path and intensity of a hurricane. By analyzing the spaghetti models, you can gain insights into the possible scenarios and make informed decisions about your safety and preparations.
When interpreting spaghetti models, it is important to consider the following factors:
The Cone of Uncertainty
The cone of uncertainty is a shaded area on the spaghetti model that represents the most likely path of the hurricane. The cone is wider at the end, indicating greater uncertainty about the hurricane’s future path.
The Number of Models
The more spaghetti models that agree on a particular path, the more likely that path is to occur. However, it is important to remember that even if all the models agree, there is still a chance that the hurricane could take a different path.
The Spread of the Models
The spread of the spaghetti models refers to how widely they are dispersed. A narrow spread indicates that there is a high level of agreement among the models, while a wide spread indicates a greater level of uncertainty.
The Intensity of the Hurricane
The intensity of the hurricane is indicated by the color of the spaghetti lines. Red lines indicate a more intense hurricane, while blue lines indicate a less intense hurricane.
Limitations of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models are a valuable tool for hurricane forecasting, but they have some limitations. One limitation is that they are not always accurate. The models are based on computer simulations, and these simulations can be affected by a number of factors, such as the quality of the data that is used to initialize the model and the complexity of the model itself. As a result, the models can sometimes produce inaccurate forecasts.
Another limitation of spaghetti models is that they can be difficult to interpret. The models produce a large amount of data, and it can be difficult to determine which data is most relevant to a particular forecast. As a result, it is important to use spaghetti models in conjunction with other forecasting tools, such as the National Hurricane Center’s official forecast.
Using Spaghetti Models in Conjunction with Other Forecasting Tools, Hurricane beryl spaghetti models
Spaghetti models can be a valuable tool for hurricane forecasting, but they should not be used in isolation. It is important to use spaghetti models in conjunction with other forecasting tools, such as the National Hurricane Center’s official forecast. By using a variety of forecasting tools, you can get a more complete picture of the potential path of a hurricane and make better decisions about how to prepare.
Case Studies of Hurricane Beryl: Hurricane Beryl Spaghetti Models

In August 2018, Hurricane Beryl formed in the Atlantic Ocean and posed a significant threat to the Caribbean and the United States. Spaghetti models were used extensively to predict the path of the hurricane and help prepare for its potential impact.
One of the most accurate spaghetti models for Hurricane Beryl was the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model. This model consistently predicted the hurricane’s path with high accuracy, even several days in advance. The ECMWF model was able to capture the hurricane’s initial movement towards the Caribbean, as well as its subsequent turn towards the United States.
Impact of Spaghetti Models
The spaghetti models for Hurricane Beryl were an invaluable tool for emergency managers and residents in the affected areas. The models helped to provide early warning of the hurricane’s potential path, allowing people to evacuate and take other precautions to stay safe. The accuracy of the models also helped to reduce anxiety and uncertainty about the hurricane’s impact.
Overall, the spaghetti models for Hurricane Beryl were a valuable tool for predicting the hurricane’s path and helping to prepare for its impact. The models were accurate and effective, and they helped to save lives and property.
